Electronic properties of isolated molecules: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
No edit summary |
|||
| Line 8: | Line 8: | ||
Special care needs to be put in setting up calculations accordingly. | Special care needs to be put in setting up calculations accordingly. | ||
* '''scf + nscf''': DFT calculations for molecules (or systems with reduced dimensionality in general) follow the same strategies discussed in the previous lectures, where scf calculations are followed by nscf runs (and perhaps by post-processing steps, as discussed below in [[Electronic properties of isolated molecules#Post processing tools]]). | * '''scf + nscf''': DFT calculations for molecules (or systems with reduced dimensionality in general) follow the same strategies discussed in the previous lectures, where scf calculations are followed by nscf runs (and perhaps by post-processing steps, as discussed below in [[Electronic properties of isolated molecules#Post processing tools]]). | ||
* '''molecule isolation''': when localised basis sets are used, this is usually the default option. Instead, when using plane-waves, periodic boundary conditions are automatically enforced and molecule isolation has to be achieved by | * '''molecule isolation''': when localised basis sets are used, this is usually the default option (and care must be used to impose periodicity). Instead, when using plane-waves, periodic boundary conditions are automatically enforced and molecule isolation has to be achieved by several strategies. aaa including vacuum in the unit cell. | ||
* '''including vacuum''': for a molecule this means that the cell to be adopted needs to account for the size of the molecule to be studied plus extra space to avoid or reduce the interaction of the molecule with its periodic replica. | * '''including vacuum''': for a molecule this means that the cell to be adopted needs to account for the size of the molecule to be studied plus extra space to avoid or reduce the interaction of the molecule with its periodic replica. | ||
Revision as of 11:21, 18 March 2021
Prev:LabQSM#Lecture 2: DFT simulations of Molecules
Calculation of molecules: Intro
At variance with bulk crystalline systems (fully periodic in 3D), molecules are finite isolated systems. Special care needs to be put in setting up calculations accordingly.
- scf + nscf: DFT calculations for molecules (or systems with reduced dimensionality in general) follow the same strategies discussed in the previous lectures, where scf calculations are followed by nscf runs (and perhaps by post-processing steps, as discussed below in Electronic properties of isolated molecules#Post processing tools).
- molecule isolation: when localised basis sets are used, this is usually the default option (and care must be used to impose periodicity). Instead, when using plane-waves, periodic boundary conditions are automatically enforced and molecule isolation has to be achieved by several strategies. aaa including vacuum in the unit cell.
- including vacuum: for a molecule this means that the cell to be adopted needs to account for the size of the molecule to be studied plus extra space to avoid or reduce the interaction of the molecule with its periodic replica.
Post processing tools
Exercises
Exercise1

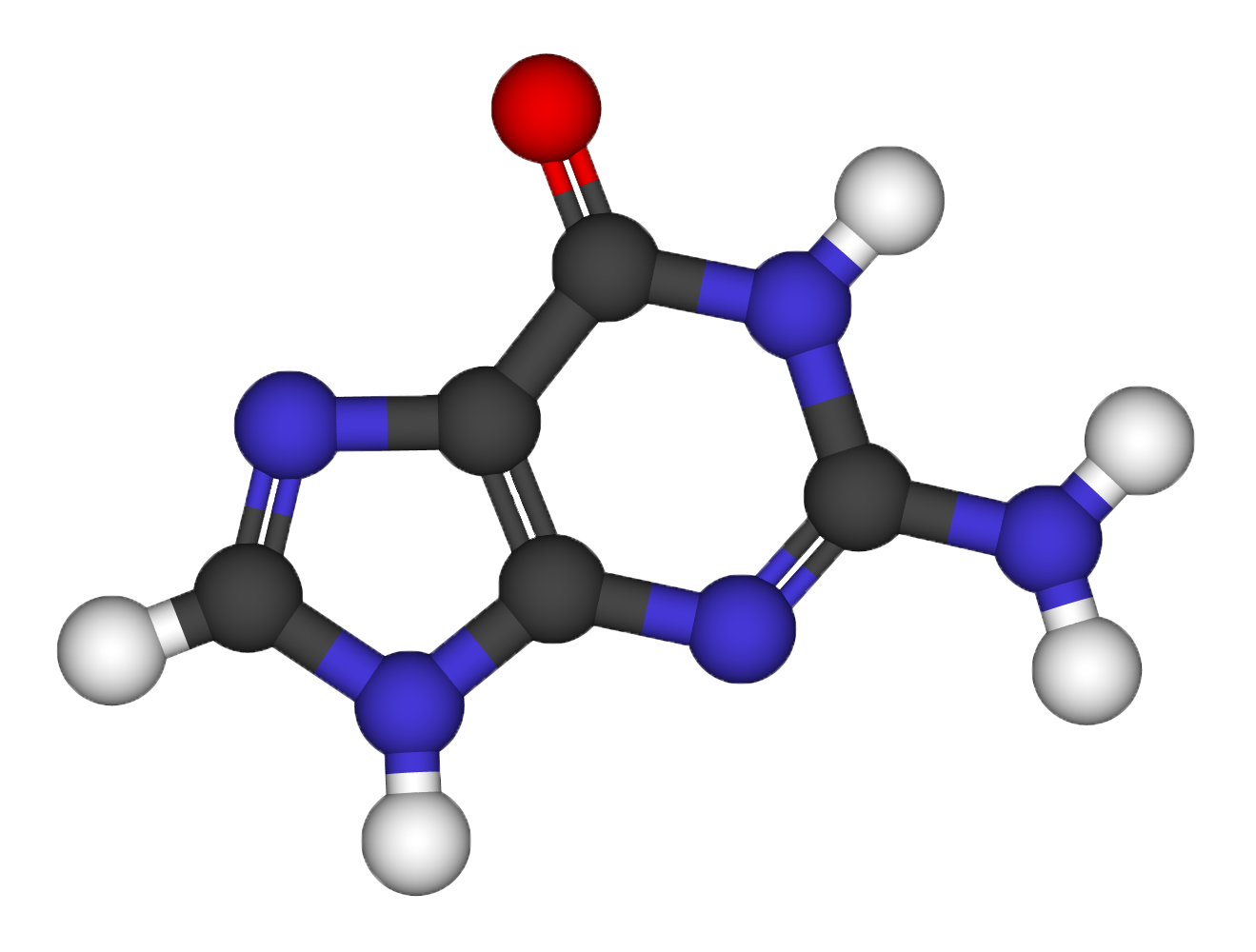
Structural relaxation of the Guanine molecule
- Use a molecular builder to find the initial molecular structure. (Avogadro)
- Classical Force Field Relaxation (using a built-in engine)
- Quantum Mechanics Relaxation refinement (Quantum ESPRESSO) (thr=10^-3)
- Use the xcrysden software to visualize the relaxation path.