Structural and electronic properties of semiconductors and metals: Difference between revisions
| Line 22: | Line 22: | ||
Diamond is a face-centered cubic structure with two C atoms at 0 0 0 and 0.25 0.25 0.25 | Diamond is a face-centered cubic structure with two C atoms at 0 0 0 and 0.25 0.25 0.25 | ||
a is the lattice parameter | a is the lattice parameter | ||
Now let's see in detail how a QE input is structured to make a total energy calculation for this system | |||
Revision as of 11:40, 1 December 2020
Prev: LabQSM#Lecture 1: Basic DFT calculations and Convergences
Structural and electronic properties of Diamond

In this tutorial we will see how to setup a calculation and to get total energies using the PW code from the Quantum ESPRESSO distribution.
Some helpful conversions:
1 bohr = 1 a.u. (atomic unit) = 0.529177249 angstroms.
1 Rydberg = 13.6056981 eV
1 eV =1.60217733 x 10-19 Joules
For all first-principles calculations, you must pay attention to two convergence parameters. The first one is the energy cutoff, which is the max kinetic energy used in wave-function expansion. The second is the number of k-points, which measures how well the continuous integral over the BZ is discretized.
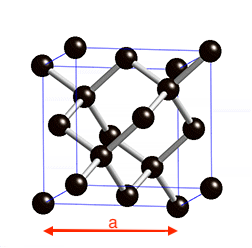
Diamond is a face-centered cubic structure with two C atoms at 0 0 0 and 0.25 0.25 0.25 a is the lattice parameter
Now let's see in detail how a QE input is structured to make a total energy calculation for this system