Difference between revisions of "Warming up with Unix commands"
| Line 22: | Line 22: | ||
==Filesystem== | ==Filesystem== | ||
| − | As seen above, the command $pwd (present working directory) shows the directory you are presently working on. | + | As seen above, the command $pwd (present working directory) shows the directory you are presently working on. Now we want to see how to navigate to other directories. This is done by using the command '''$cd''' (change directory) followed by a path. |
| − | + | If we want to move for instance to the folder LabQSM we need to provide its path. A path is the address of a file or a folder. | |
| − | + | We can use an '''absolute path''': | |
| − | + | $cd /home/max/LabSQM | |
| − | + | or a '''relative path''' | |
| − | + | $cd LabSQM | |
| − | You can navigate up on level by typing: | + | provided that we are already in /home/max |
| + | |||
| + | You can then navigate up on level by typing: | ||
$cd .. | $cd .. | ||
Revision as of 13:47, 20 November 2020
Getting Stearted
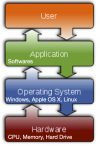
In this lesson, you will learn some basic commands of the Unix operative system. The operating system (OS) is the system software that manages computer hardware, software resources, and provides common services for computer programs, i.e. allow the communication between hardware and software. In order to use a computer, you need an OS. At this moment you are using a Virtual Machine containing the Ubuntu OS, a Linux distribution, a Unix-like OS. The command used in Linux and Unix they are essentially the same.
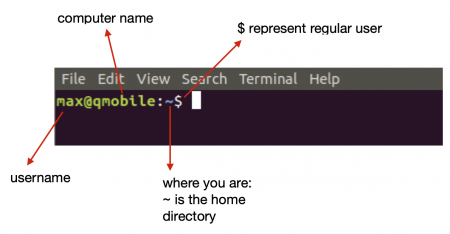
If you open a terminal window a prompt will appear where you can type your command. A snapshot of the prompt is shown here below:
You can inspect your environment by typing the following commands:
- $ whoami # (my username)
- $ hostname [-A] # (machine name)
- $ pwd # (current directory)
- $ ls [-ltr] # list files and dirs
- $ ps # running processes
- $ top # more on running procs
- $ date # show date and time
Filesystem
As seen above, the command $pwd (present working directory) shows the directory you are presently working on. Now we want to see how to navigate to other directories. This is done by using the command $cd (change directory) followed by a path.
If we want to move for instance to the folder LabQSM we need to provide its path. A path is the address of a file or a folder.
We can use an absolute path:
$cd /home/max/LabSQM
or a relative path
$cd LabSQM
provided that we are already in /home/max
You can then navigate up on level by typing:
$cd ..