Difference between revisions of "Solution LAB1 Al"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
| (One intermediate revision by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | * Back to the previous page: [[Structural and electronic properties of semiconductors and metals # | + | * Back to the previous page: [[Structural and electronic properties of semiconductors and metals #A metallic system: Aluminium]] |
[[File:Al conv.png|450px]] | [[File:Al conv.png|450px]] | ||
| + | |||
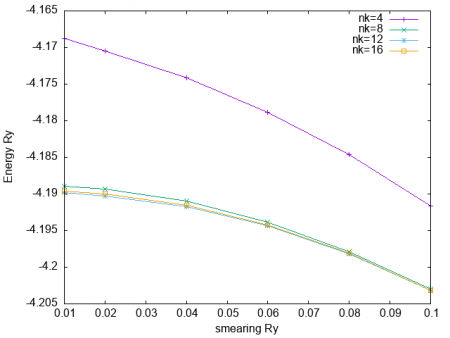
| + | What we can note is: | ||
| + | |||
| + | * Larger k-points grids are needed with respect the insulator case | ||
| + | * Notice that you cannot reduce the broadening too much: the energy levels must have some overlap, or else the advantage of broadening is lost. A small broadening is needed, but it can be reduced only if the k point grid is dense enough | ||
| + | * Note that the number of bands (Kohn-Sham states) is no longer automatically set to the number of electrons divided by 2, but a larger number of bands is considered. | ||
| + | * Note also that for metallic system the Fermi energy is reported in the output | ||
Latest revision as of 11:36, 16 December 2020
- Back to the previous page: Structural and electronic properties of semiconductors and metals #A metallic system: Aluminium
What we can note is:
- Larger k-points grids are needed with respect the insulator case
- Notice that you cannot reduce the broadening too much: the energy levels must have some overlap, or else the advantage of broadening is lost. A small broadening is needed, but it can be reduced only if the k point grid is dense enough
- Note that the number of bands (Kohn-Sham states) is no longer automatically set to the number of electrons divided by 2, but a larger number of bands is considered.
- Note also that for metallic system the Fermi energy is reported in the output